The Async Events
An Async Event is executed asynchronous after a processing life-cycle. In difference to Follow-Up Events the process instance will be persisted in a new status before a async event is executed.
Async Events are modeled as BPMN Boundary Events.
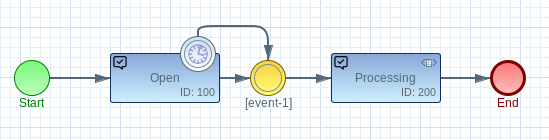
In BPMN2 the definition of a Async Event can be modelled in the ‘Timer Definition’ like this:

BPMN 2.0 Definition
<bpmn2:boundaryEvent id="BoundaryEvent_1" name="" attachedToRef="Task_1">
<bpmn2:outgoing>SequenceFlow_8</bpmn2:outgoing>
<bpmn2:timerEventDefinition id="TimerEventDefinition_2">
<bpmn2:timeDuration xsi:type="bpmn2:tFormalExpression" id="FormalExpression_4">1000</bpmn2:timeDuration>
</bpmn2:timerEventDefinition>
</bpmn2:boundaryEvent>
<bpmn2:sequenceFlow id="SequenceFlow_8" sourceRef="BoundaryEvent_1" targetRef="IntermediateCatchEvent_3"/>
Note: Imixs AsyncEvents are designed for short-running, time-critical transactional actions—typically ranging from a few milliseconds to a few minutes. They are ideal for triggering quick asynchronous follow-up tasks within a separate workflow transaction. For long-running or recurring processes lasting hours, days, or even years, the Workflow Scheduler is the recommended solution, as it is specifically built for long-term timer and background job execution.
The AsyncEventProcessor
The AsyncEventProcessor is a managed execution service observing the life cycle of a process instance. If a process instance reaches a task with a Async Event a asynchronous log event will be created and the targetEvent will be executed after the processing life-cycle is completed.
The TransactionID
A workitem entity is holding a $transactionID identifying the last processing life-cycle. An AsyncEvent is only processed in case the $transactionID matches the last transactionID from the workitem. In case the $transactionID has changed the AsyncEventProcessor discards the eventLog entry. This mechanism ensures that AsyncEvents are not fired twice or outside the corresponding status.
Configuration
The AsyncEventProcessor runs on a scheduled base defined by the following environment settings:
ASYNCEVENT_PROCESSOR_INTERVAL - timeout period in milliseconds
ASYNCEVENT_PROCESSOR_INITIALDELAY - To enable the Processor
ASYNCEVENT_PROCESSOR_ENABLED - must be set to true (default=false).
ASYNCEVENT_PROCESSOR_DEADLOCK - deadlock in milliseconds (default 1 minute)
To prevent concurrent processes to handle the same workitems the batch process uses a Optimistic lock strategy. The expiration time on the lock can be set by the environment variable ASYNCEVENT_PROCESSOR_DEADLOCK.
The EventLogService and Rest API
You can create, read or remove events with thes EventLogService. This service provides methods to programmatically manage events. See the section EventLogService for details.
@EJB
EventLogService eventLogService;
....
eventLogService.createEvent(workitem.getUniqueID(), "MY_TOPIC");
Additionally you can access the event logs also via the Imixs Rest API. This allows you to process events externaly or exchange events between different workflow instances.
EventLogClient client = new EventLogClient(externalBaseURI);
// set credentials..
eventLogClient.createEventLogEntry("MY_TOPIC", workitem.getUniqueID(), myDataObject);
Find more details in the section EventLogService.
