The Imixs Rule Engine
The Imixs Workflow project provides a powerful, fast and very flexible rule engine to evaluate business rules in a BPMN model. Business rules can be written in different popular languages and can be combined with additional features and libraries.
The Imixs Rule Engine is based on the GraalVM adn integrates seamless into the Imixs Workflow engine.
The Core RuleEngine
The Imixs Core RuleEngine evaluates any kind of business rules based on the build-in GraalVM script engine. A business rule can be written in any script language supported by the GraalVM. The RuleEngine can be used in a BPMN event to evaluate business rules based on the Imixs RulePlugin.
The Imixs Core RuleEngine provides direct access to the item values from a given current workItem or BPMN event. The results of a business rules are stored in an object named result which is mandatory.
// test the value of the workitem attribute 'name'
var result={}; result.isValid = ('Anna'==workitem.getItemValueString('name'));
A business rule can add additional values to the JSON based result object:
var result={ someitem:'Hello World', somenumber:1};
These additional items will be stored in the current process instance. See the section Imixs RulePlugin for further details.
Calling the Core Rule Engine Programmatically
You can call the Imixs Core RuleEngine programmatically from your java code. The method evaluateBusinessRule() expects a script containing the business rule and the optional objects workitem and event to be evaluated in the script. See the following example:
ruleEngine = new RuleEngine();
ItemCollection workitem = new ItemCollection();
workitem.setItemValue("name", "Anna");
// define a script
String js = "var result={}; if ('Anna' == workitem.getItemValueString('name')) result.colleague='Melman';";
// evaluate the business rule
workitem = ruleEngine.evaluateBusinessRule(js, workitem, null);
Assert.assertNotNull(workitem);
Assert.assertEquals("Melman", workitem.getItemValueString("colleague"));
evaluateBusinessRule
The method evaluateBusinessRule evaluates the business rule. The method returns the instance of the evaluated result object which can be used to continue evaluation. If a rule evaluation was not successful, the method returns null.
workitem = ruleEngine.evaluateBusinessRule(js, workitem, event);
evaluateBooleanExpression
The method evaluateBooleanExpression can be used to evaluate a boolean expression. The method takes a workitem as an optional argument and returns a boolean value indicating the result of the business rule.
ItemCollection workitem = new ItemCollection();
workitem.setItemValue("budget", 1000);
boolean result = ruleEngine.evaluateBooleanExpression("(workitem.getItemValueDouble('budget')>100)", workitem);
Assert.assertTrue(result);
All kind of boolean business rules are mainly used to evaluate conditional events.
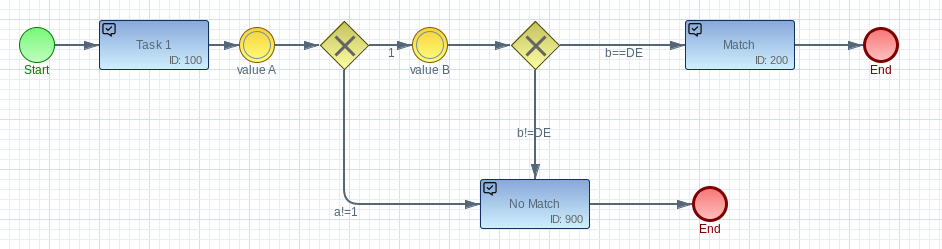
Evaluate the Processing Life Cycle
The Imixs WorkflowKernel is using the RuleEngine to navigate through the BPMN model during the processing life cycle. In case an Event is followed by a Gateway with conditional events, the RuleEngine evaluates these rules to compute the target element based on the business data provided by the process instance.
A condition in a BPMN business rule is evaluated to a boolean indicating if the condition is true or false:
(workitem.getItemValueDouble('budget') > 100) && ('finance'.equals(workitem.getItemValueString('category'))
See the section conditional events to learn how you can model business rules.
Simulating the Processing Life Cycle Programmatically
The WorkflowKernel also provides the method eval() to simulate the outcome of a specific model situation. You can call this method to evaluate the target Task Element of a process instance:
ItemCollection workitem = new ItemCollection();
workitem.model(MODEL_VERSION).task(100).event(10);
workitem.setItemValue("a", 1);
workitem.setItemValue("b", "DE");
ItemCollection targetTask = workflowKernel.eval(workitem);
// evaluate rule
Assert.assertEquals("Match", targetTask.getItemValueString("name"));
