How Imixs-Workflow works
Imixs-Workflow is an open source workflow engine for human-centric business process management (BPM). Human-centric BPM means to support human skills and activities by a task orientated workflow-engine. The Imixs-Workflow project provides a framework for the development of human-centric business applications. The Imixs-Workflow engine can be embedded in a Java EE application, or run stand-alone as a web-service in a microservice architecture.
BPMN 2.0
Imixs-Workflow is based on BPMN 2.0 which is be used to describe a business process on different levels. In a human-centric business process, the BPMN “Task” element is used to describe the activity to be processed by the human actor, and the BPMN “Event” element is used to describe the transition form one state into the next.
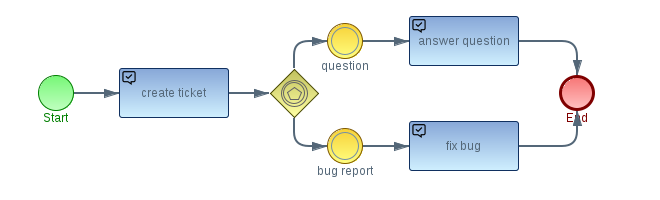
Based on the model, the Imixs-Workflow engine controls the state of a business object and guides the different actors through the process. The Imixs-Workflow provides all the necessary information and decisions arising from the processing of a business task. With the help of BPMN 2.0 different business situations can be described easily and so the implementation and maintenance of a business application becomes even faster and more flexible.
The Actors
The main objective of a human-centric workflow engine is to support the human actors with relevant information about the process and to ensure the business process is aligned to the predetermined rules:
- What is the current status of a business process
- Who is the owner for a business process
- Who need to be informed
- What happened so far to the business process
- Who is allowed to access and modify data
In that way Imixs-Workflow assists users in starting a new process, finding and processing open tasks and helps users to complete current jobs in the defined way. The Workflow Engine automatically routes open tasks to the next actor and notifies users about new tasks depending on the current process definition.
Each business process defines different users to be involved. These users are called the actors, which are interacting with the Workflow Management System during a business process. Actors can either start, update or read information about a process instance. The Imixs-Workflow allows to grant actors access to a process instance depending on the process flow. This means also that users who are not involved will not be allowed to access a running process instance. Thus Imixs-Workflow provides also a security layer to secure business data based on a process model.
The Concept
The Imixs-Workflow engine allows the linking of business data to a business process. For this purpose, the project offers some basic concepts, which simplify the development of business applications.
The Workitem
A running process instance inside a Workflow Management System is called ‘Workitem’. Each Workitem can assume different states during a business process and can contain any kind of business data. If a Workitem is still processed and yet not finished, the Workitem is called a ‘running process instance’. The status of a workitem is defined by the process model and is controlled by the workflow engine.
The Process Model
The Process Model (or Workflow Model) defines which status a process instance can present during its life-cycle. Each time a Workitem is processed, the Workflow Management System assigns a new status (Task). The transition form one status into another is defined by the Workflow Activities (Event).
The Workflow Engine
The Workflow Engine persists and controls each process instance depending on the model definition. The Workflow Engine ensures that a workitem is always in a state defined by the process model and can not change its status in a way which is not defined by the model. The Workflow Engine also routes the workitem to the next actor and sends notifications if defined by the model.
Tasklist and Statuslist
A Workflow Management System provides views of all running process instances. A ‘tasklist’ contains all open tasks from the view of an individual actor. The statuslist provides the user with the latest status information about running process instances. There are a lot of different views allowing the actor to navigate through the running process instances.
Getting started…
There are several ways how you can benefit from Imixs-Workflow. The following section gives you a short guideline how to find out the best way to use Imixs-Workflow in your own project.
Using the Imixs-Workflow Engine out of the Box
Using Imixs-Workflow out of the Box is a good starting point to run the workflow engine without modification or Java EE development. You can start with the Imixs-Workflow Sample Application if you don’t want to develop a new project from scratch.
Before you begin, consider the following:
- Provide a database where the workflow model and the workitems can be stored
- Configure a security realm to grant access for actors
- Define a workflow model using the Imixs-Workflow-Modeler
- Deploy the workflow application on an application server
Using Imixs-Workflow in a Java EE Project
Using Imixs-Workflow in a Java EE project is the typical way to extend your own java project with the functionality of a workflow engine. In this kind of usage you develop your own workflow application. Inside your application you integrate the Imixs-Workflow Engine to provide the typical functionality of a Workflow Management System.
To integrate Imixs-Workflow engine in an JEE application consider the following steps:
- Add the Imixs-Workflow jar files to your application.
- Add the Imixs-RestService into your application.
- Deploy your application together with the Imixs-Workflow on a application server
Read the Deployment Guide about how to deploy the Imixs-Workflow engine into an enterprise application (EAR).
Contribute to the Imixs-Workflow project
You can also help in developing the Imixs-Workflow project or use the results of the project to implement new components. In this case you extend the implementation with additional features or just add a different behavior. So in different of the usage described before, you need more than a running instance of the Workflow Engine or the Java EE libraries. In this kind of usage you should check out the source code packages from GitHub and set up a Java EE Project. The source code include also some JUnit tests which can help to test different behaviors of the engine.
See the Imixs Workflow community site on GitHub for source code or ask questions in the issue tracking tool.
